A voltage multiplier is an electronic circuit that converts low-voltage AC power into DC voltage that is higher by using capacitors and diodes are assembled into a specific network voltage multiplier can be used as a bias voltage of a few millivolts to millions of volts as for high-energy physics research interests and security testing against lightning. The most common voltage multiplier is a series of half-wave multiplier, or known by the flow Villard (actually discovered by Heinrich Greinacher).
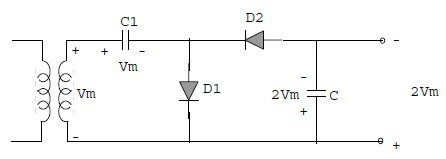 |
| image folder 2 times the half-wave voltage to the diode |
At the time of the transformer secondary voltage of positive polarity (positive half cycle), then the diodes D1 and D2 deliver not deliver. Ideally diodes being considered deliver short circuit. Therefore C1 charged voltage through D1 until it reaches Vm with polarity
At the time of the next half cycle is a negative cycle, the diodes D1 and D2 deliver not deliver. Therefore, the capacitor C2 charged voltage of the transformer secondary for Vm and Vm amount of C1, so that a total of 2 Vm. If the given output load resistor (RL), the voltage at the end of the C2 down during the positive cycle and refilled up to 2 Vm during the negative cycle. The output waveform at the end of the C2 is like a form of half-wave rectifier output with peak inverse filter C. Voltage (PIV) for each diode is 2 Vm.
0 Response to "Voltage Multiplier"
Post a Comment